Virus
|
Duncan MacDonald
Jakarta 3 February 2010
What is a virus ?
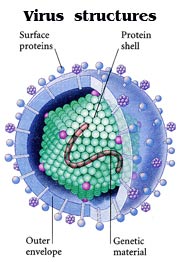 Viruses are the smallest infectious organism. They are so tiny that millions could fit inside a human cell. Viruses are only capable of reproducing inside a living cell, called a host cell, that they invade. A virus consits of little more than a single or double strand of genetic material surrounded by a protein shell. However some types of virus also have a protective outer envelope.
Viruses are the smallest infectious organism. They are so tiny that millions could fit inside a human cell. Viruses are only capable of reproducing inside a living cell, called a host cell, that they invade. A virus consits of little more than a single or double strand of genetic material surrounded by a protein shell. However some types of virus also have a protective outer envelope.Viruses cause many diseases including the common cold, influenza, measles, mumps, chickenpox, herpes, AIDS, polio, rabies and COVID-19. Antiviral drugs are effective against them and many viral diseases are controlled by means of vaccines. [1]
Common Cold
An infection of the nose and throat that can be caused by many viruses. There are at least 200 highly contageous viruses that are known to cause the common cold. These viruses are easily transmitted in the minute airborne droplets sprayed from the coughs or sneezes of infected people. In many cases the viruses are spread to the nose and throat by hand-to-hand contact with an infected person.About half the population in US and Europe develop at least one cold each year. Children are more suseptable to colds than adults as they have not yet developed immunity to the most common viruses. Also viruses quickly spread very quickly through communities such as nurseries and schools.
What are the symptoms ?
Initial cold symptoms usually devlop between 12 hours and 3 days after infection. Symptoms usually intensify over 24 - 48 hours, unlike Influenza (see below) which worsen rapidly within a few hours .
If you have a cold the symptoms may include;
• Frequent sneezing
• Mild fever and headache
• Sore throat and sometime a cough
• Runny nose with a clear watery discharge that later becomes thick and green coloured
In some people, a common cold may be complicated by a bacterial infection such as Bronchitis (infection of the chest), or Sinsitis (infection of the sinuses).
What can I do ?
Most people recognise their symptoms as a common cold and do not seek medical advice. Despite a great deal of scientific research, there is no cure for the common cold. Over-the-counter drugs can releave the symptoms. These drugs include painkillers, to reduce fever and releave headaches; decongestants, to clear a stffy nose; and cough remedies, to soothe a tickling throat.It is important to drink pleanty of fluids, particularly if you have a fever. Many people take large quantities of vitamin C to prevent infection and treat the common cold, but any benefit from this popular remedy is unproved.
If your symptoms do not improve in a week or your child is no better in 2 days, you should consult a doctor. If your child has a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic, although they are ineffective against viruses.
The common cold usually clears up without treatment within 2 weeks, but a cough may last longer. [2]
Antibiotics have no effect against viruses, which are the cause of colds and flu
Influenza (flu)
An infection of the upper respiratory tract (airways) commonly known as the flu.Influenza is a highly contagious viral disease that tends to occur in epedemics, during the winter. The infection can be transmitted easily in airborne droplets from the coughs and sneezes of infected people. Influenza can also be transmitted from person to person through direct contact e.g. shaking hands, or pressing buttons in lifts after an infected person [hint: use your knuckles].
Many differenct viral infections can result in mild flu-like symptoms, but true influenza is caused by two principal types of influenza virus: A and B. The type A virus in particular often changes its structure (mutates) and produces new strains to which very few people have immunity.
The number of flu cases vary year to year, but particularly virulent strains can spread worldwide and cause millions of deaths in major outbreaks, known s pandemics. Twentieth century pandemics include Spanish Flu of 1918 (the worst pandemic the world has known in recorded history), Asian flu in 1957, Hong Kong flu in 1968, Russian flu in 1977 and Mexican or Swine Flu 2009
What are the symptoms ?
The symptoms of influenza develop 24 - 48 hours following infection. Many people believe they have influenza when they only have a common cold. However the symptoms of flu are are far more severe than those of a cold.The first symptoms may be slight chills. Other symptoms, which develop later and worsen rapidly injust a few hours may include;
• High fever, sweating and shivering
• Aching muscles, especially in the back
• Severe exhaustion
• Frequent sneezing, stuffy or runny nose, sore throat and cough
Following a flu attack, tiredness and depression are often experienced, after other symptoms have disappeared.
The most common complications are bacterial infection of the airways (acute broncitis) and lungs (pneumonia). Such infections can be life-threatening to people in high risk groups - those with long-term heart or lung disease and people with lowered immunity such as HIV and AIDS.
What can be done ?
For most healthy people, the best way to relieve the symptoms of influenza is to rest in bed, drink pleanty of cool fluids and follow the advice for bringing down a fever. A fever is a body temperatur e above 38ºC (100ºF)
e above 38ºC (100ºF) Discomfort can be relieved by over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol.
Ensure the patient receives pleanty of fluids. If self help remedies do not relieve the symptoms your doctor may prescribe antiviral drugs such as amantadine, which usually have a rapid effect against influenza viruses provided they are given within 24 hours of onset of the symptoms.
You should see your doctor immediately if you have breathing difficulties or your fever lasts longer than 2 days. Be aware: antibiotics have no effect on the influenza virus itself.
Should I take flu shots ? They are importaint, especially for those in the high-risk categories. You cannot get flu from a vaccine. This is because the virus used in the vaccine is dead. Your body however may react mildly: a slight fever within 24 hours or a swollen, red or tender area where the shot was administered for a couple of days. [3]
Conclusion
If there are no complications, most of the symptoms of influenza usually disappear after 6 - 7 days, although a cough may persist for over 2 weeks. For anyone in the high-risk groups the complications of influenza may be life threatening.In epidemics, death from associated pneumonia is very common.





